Data
Aug 13, 2020
Better Experiences and Better Outcomes: 6 Key Steps to Building and Leveraging a Single Customer View

A single customer view is a must-have to compete in today’s customer-centric world. The ability to utilize data from numerous sources to better understand your customers, their tendencies, and how they interact with your brand can provide invaluable information to help guide marketing efforts. Today’s marketer can leverage thousands of cutting-edge tools to better enable a modern marketing experience. However, most marketers lack a fully unified, single customer view to realize the maximum benefits of these tools.
A single customer record is created by ingesting information from multiple data sources and stitching that data together based on the identity of the customer, providing a single source of truth of customer information across your organization. This can enable many business functions, but we will specifically explore the marketing uses and benefits of the single customer view in this blog. There are six key steps to creating a single customer view for an organization:
Customer Data Ingestion
Identity Resolution
Customer Profile Maturation
Segmentation
Predictive Scoring
Activation
Once you’ve created a single customer view, you can then utilize that data to provide personalized content to each customer and ultimately increase your customers’ lifetime value and brand loyalty. Targeting customers individually, rather than as a whole, allows companies to provide unique experiences specifically tailored to each customer, resulting in increased conversion, repurchase, and retention rates. The ability for an organization to act on their customer data is valuable because it enables better investment of marketing dollars in the largest revenue growth drivers over time.
To explore the process of implementing a single customer view, let’s look at an example retail company, SCV Co., who is looking to enhance their customers’ experiences and increase marketing effectiveness using this strategy.
1. Customer Data Ingestion
The first thing for SCV Co. to consider when creating a single customer view is what data is available to them and what additional information they would like to capture about their customers. The goal is to gather key pieces of information that will enable you to learn more about your customer. Once you have gathered this data, you can then unify the data in a way that will provide insight into the end-to-end customer experience, resulting in a deeper understanding of your customer and ultimately leading to a more personalized experience.
The collection of both first party data (customer data captured directly by SCV Co.) and third party data (data captured by another organization or platform) is crucial for creating a comprehensive, unified view of the customer. First party data provides foundational knowledge about SCV Co.’s current customers, while third party data allows SCV Co. to expand upon their target audience. Coupling first party data with third party data will enable SCV Co. to create a holistic view of their customer.
One key source of data for creating this holistic view is customer engagement data captured across all touchpoints that the customer has with the brand. As the customer continues to interact with the brand, more customer engagement data will be captured, enabling SCV Co. to learn more about the customer and enhance the customer’s profile. Combining this customer engagement data with additional first party and third party data, such as purchase history, customer feedback data, demographic data, geographic data, and social media data, will give SCV Co. a deeper understanding of their customers’ overall journey, which will enable them to provide more relevant customer experiences and ultimately improve brand loyalty.
Once SCV Co. has determined what customer data to capture, the next step is to determine how to gather and store that data. Data warehouses, data lakes, and customer data platforms can be used to store SCV Co.’s customer data and are able to consume and consolidate the vast amounts of data from different ingestion methods (e.g., large clickstream data files, near-real time APIs, etc.). Determining which technologies work best for SCV Co.’s organization will require an analysis of their current state, their priority use cases, and their ultimate end goal.
As SCV Co. begins to collect, store, and use this customer data, they will need to consider customer preferences, data security, and relevant consumer privacy regulations (GDPR and CCPA). Properly following customers' desires for the collection, storage, and utilization of their data will enable relevant delivery of valuable content or personalizations, incentivizing the customer to provide additional first party data.
Now that SCV Co. has determined their data needs, they will need to determine how to stitch the customer data together.
2. Identity Resolution
Identity resolution is a key step in creating a single customer view. It is the process of connecting unique identifiers to each customer from individual interactions across different data sources and tying them together to create a unified, single customer record.
This process will enable SCV Co. to transform their large amounts of raw, unidentified data into unified customer profiles that provide a holistic view into each customer. Identity resolution doesn’t necessarily mean that SCV Co. knows specifically who “Customer A” is, it just means that they’re able to tie multiple pieces of previously disparate data to the same customer, regardless of who that customer is. Depending on the type of data that they have access to, SCV Co. can use a variety of strategies for tying together customer records, including:
Joining data sets based on an internal global identifier (e.g., Customer ID, loyalty number, etc.)
Tying together records using “fuzzy logic” or combinations of other pieces of data
Using algorithms to suggest probable matches
Utilizing an external service (e.g., LiveRamp, etc.) to assist in stitching together the data
Once SCV Co. has brought together the data into an identified, holistic record, also called a golden customer record, they will continue to capture additional data about their customers from each interaction.
3. Customer Profile Maturation
As a customer continues to interact with a brand, more information about the customer will become available. Interactions with a brand can vary immensely – examples can range from opening an email from the company, clicking on a targeted ad, viewing a product on the website, or making a purchase. The image below shows an illustrative path of a journey of one of SCV Co’s customers, Jane Doe. As you can see, each interaction with this customer results in more information being captured, from the initial click of a Facebook ad all the way to the purchase, ultimately becoming a known customer.
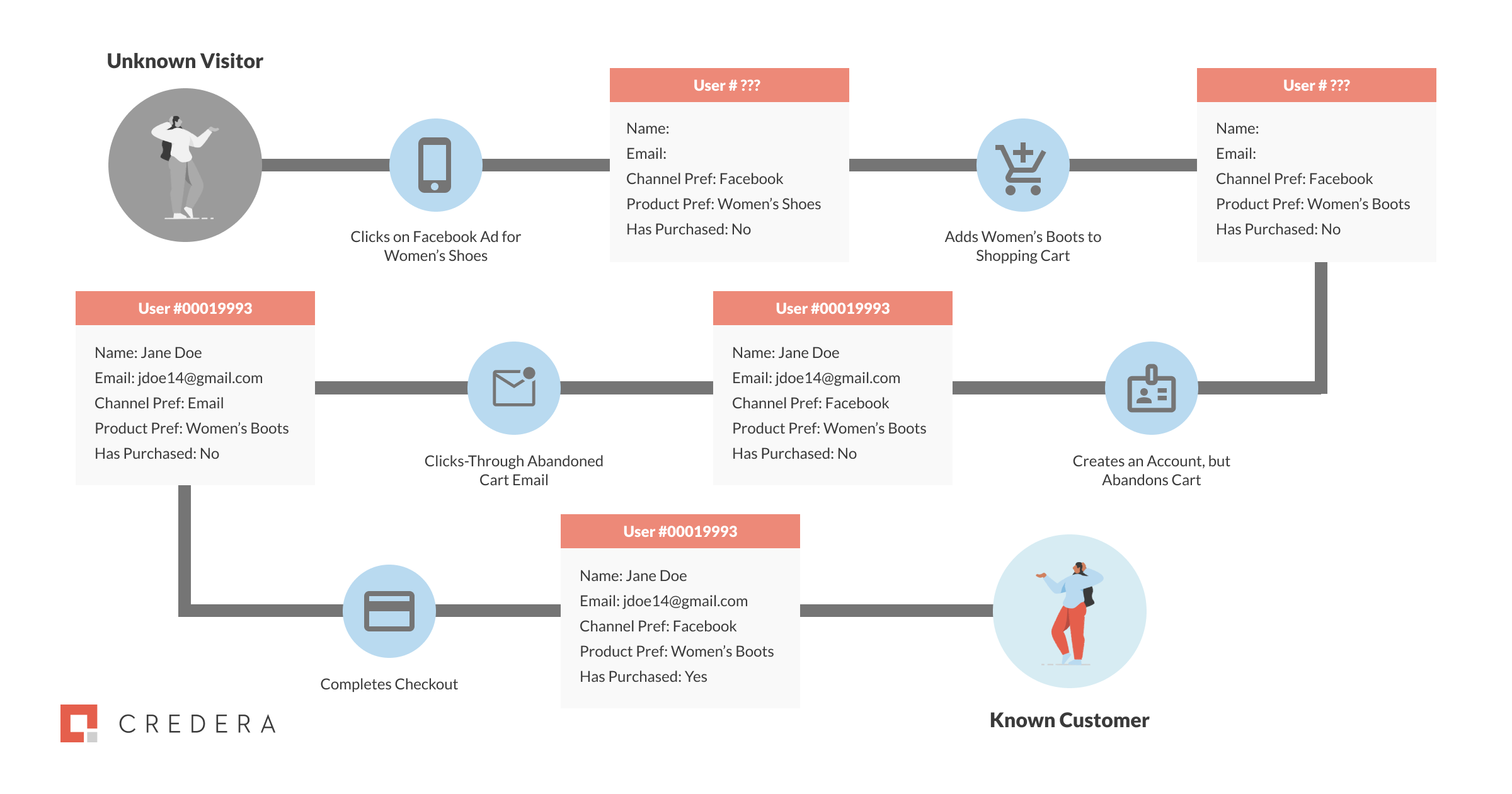
As Jane Doe continues to interact with the SCV Co. past the point of purchase, they can continue to enhance her profile. The next step for SCV Co. will be utilizing additional methods of scoring and segmentation to market to her more effectively.
4. Segmentation
Customer segmentation is the process of grouping customers based on defining characteristics of their behaviors. Simple segmentation methods utilize the foundational information we know about a customer, such as “gender” or “recently purchased products,” to group them and allow for slightly targeted marketing materials, enabling a customized user experience with the SCV Co. brand.
A slightly more complex method of segmentation is called micro-segmentation. This method allows SCV Co. to group customers into more specific groups based on more detailed, layered segmentation criteria (e.g., “25-35 year-old women in the NYC area who’ve made a purchase in the last 30 days”, etc.). Both of these methods are reactive strategies based on previous behaviors of the customer.
A third type of segmentation, predictive segmentation, utilizes machine learning and customer scoring (described next) to predict behaviors of the customers, such as “likely to convert” or “at risk”, enabling your brand to react before the action happens. This forward-thinking strategy can be extremely valuable in capitalizing on pivotal moments in the customer’s journey.
5. Predictive Scoring
Customer scoring utilizes machine learning scoring models to derive insights from existing customer attributes to predict future customer behaviors. These models are refined over time as predicted behaviors are compared to actual outcomes. An example of a scoring model SCV Co. could utilize would be the hypothesis that historical order value and website visits in the last 7 days were predictive of an imminent purchase.
As they watch the model over time, the company sees that the historical order value wasn’t as predictive of imminent purchase as the number of days since the customer’s last purchase. SCV Co. would then refine their model to look for these updated criteria when predicting future purchases. This predictive modeling can be utilized in creating customer segments and leads into predicting the next best action for a customer.
6. Activation
Now that SCV Co. has captured more robust information about their customers and utilized that information to divide customers into homogeneous groups utilizing segmentation and scoring, they can activate on this data to target them more effectively.
Even with this more personalized approach, SCV Co. is still grouping customers based on a few characteristics and providing the same experience to all customers who fit a certain profile. A way to take this type of marketing strategy to the next level is to utilize machine learning to identify the next best action for a customer based on how other similar customers have interacted with the brand.
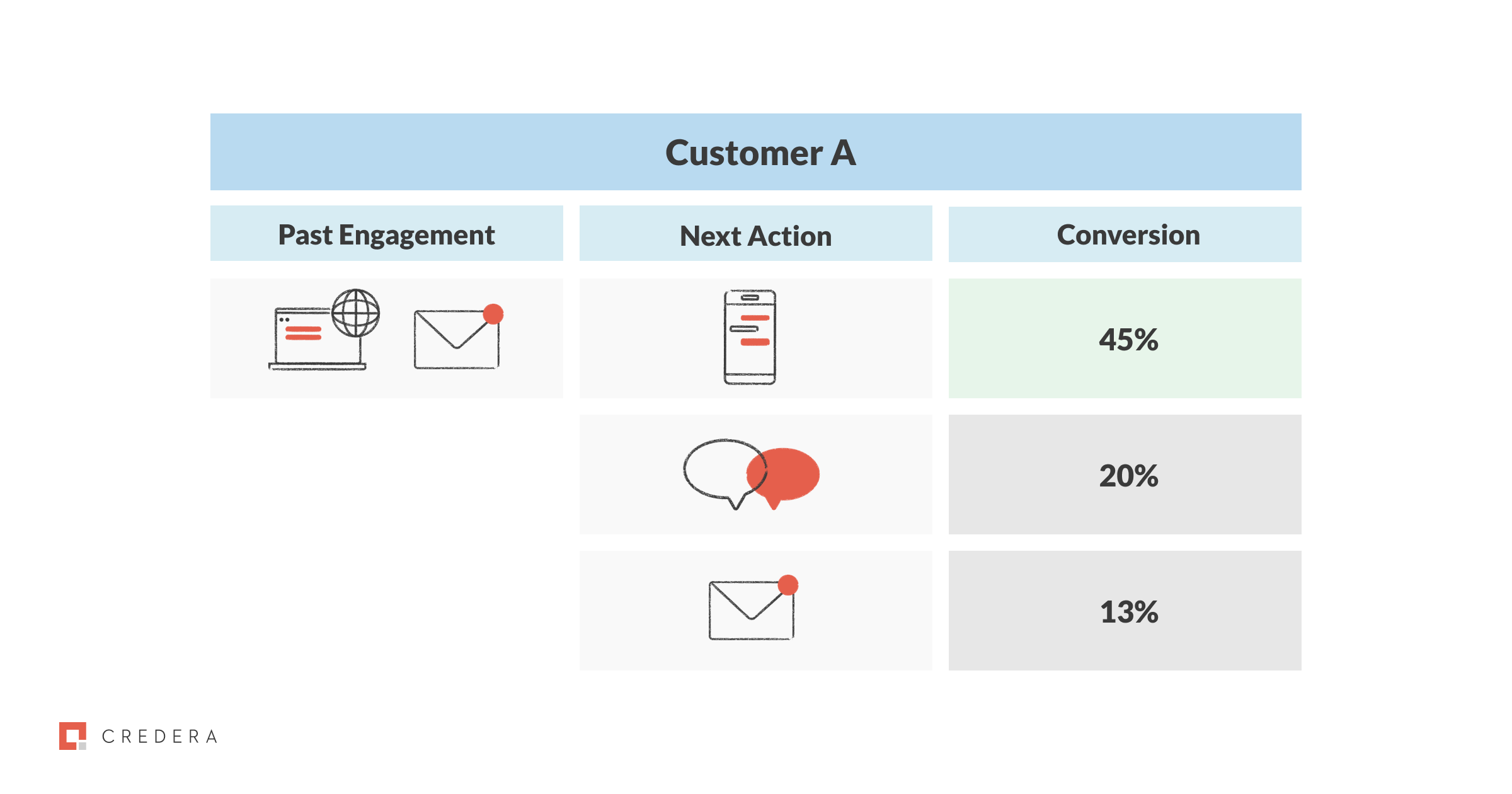
Let’s use Customer A as an example – Customer A has opened an email from SCV Co. and has visited SCV Co.’s website. The ML algorithm knows that Customer A is interacting with the brand similarly to Customer B and Customer C. The ML algorithm can see that Customer B converted and bought something after they were sent a text message, and Customer C never bought anything even after receiving multiple additional emails.
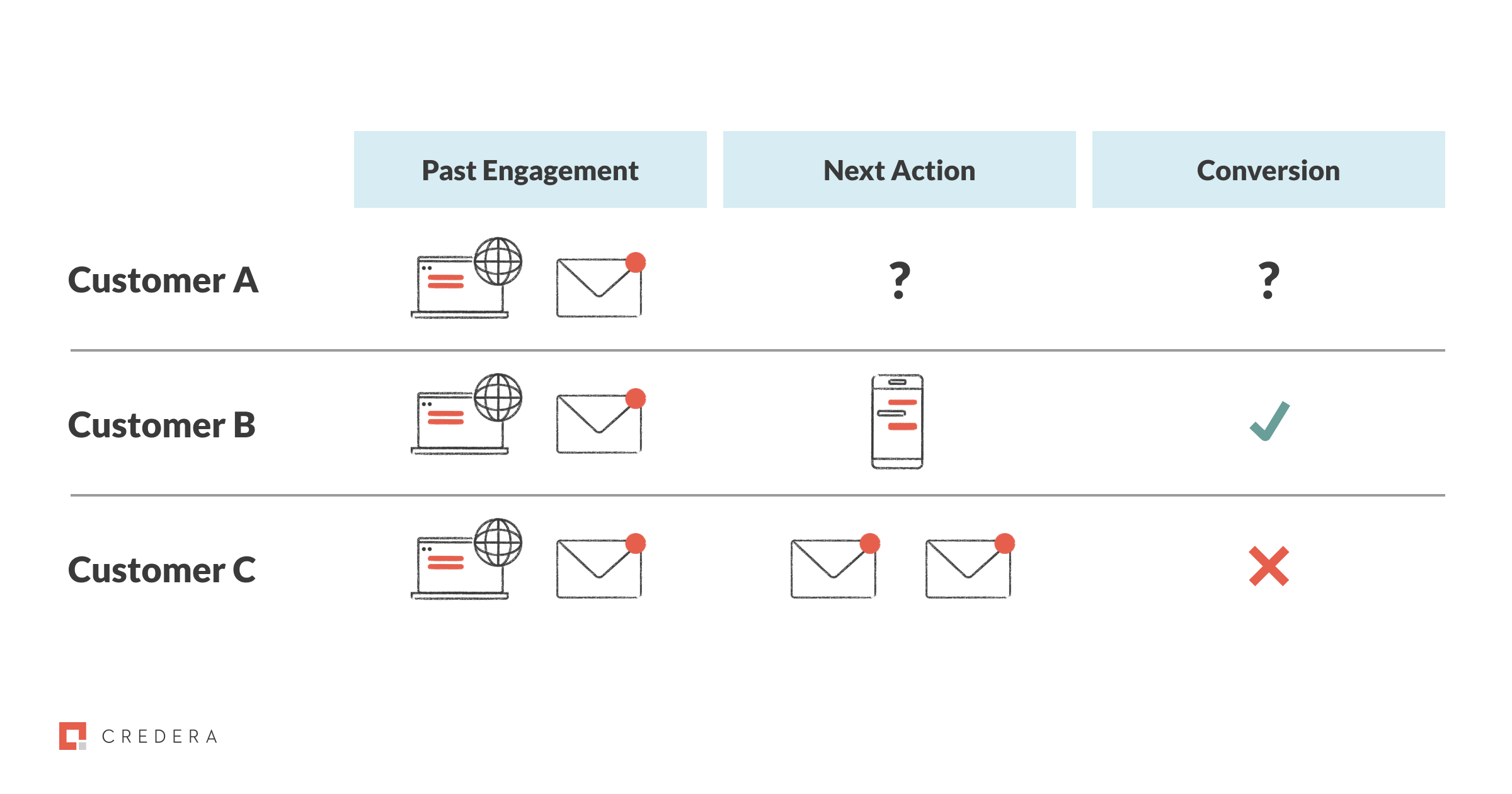
The algorithm would then determine that the next best action for Customer A would be to send them a text message, since this next best action had the highest rate of success for conversion for customers that look like Customer A, B, and C.
The most effective and mature marketing journeys utilize multiple channels of engagement, creating an omnichannel presence. To achieve this omnichannel presence, SCV Co. should determine the types of journeys that they want to engage their customers in and then develop content for all channels associated with those journeys.
To determine which journey/path each customer will be sent down, there are triggers in place that are activated when a customer performs a certain action (e.g., recently made a purchase, chatted with customer service, abandoned items in cart, etc.). The triggers watch for additional interactions across various channels, and based on each interaction, it determines the next best action and the best channel for delivery for that customer.
The journey for a customer goes from being a straight-line, generic experience to a complex, omni-channel experience that the algorithms are assembling together, learning from, and refining over time. As you can expect, the combination of all of these technologies allows for higher efficiency and more personalized engagement with customers.
Looking Forward
Throughout this blog, we explored the data, tools, and processes for implementing and utilizing a single customer view to provide remarkable customer experiences. A single customer view allows brands to develop a deeper understanding of their customers, personalize customer experiences, enhance marketing effectiveness, and ultimately increase customer lifetime value.
We hope this post has helped you gain a high-level understanding of how to create and leverage a single customer view to enhance marketing capabilities. For more information about how a single customer view fits into the larger MarTech architecture, check out this series.
If you’re interested in achieving a single customer view in your organization, we’d love to help! Please reach out to us at findoutmore@credera.com.
Contact Us
Ready to achieve your vision? We're here to help.
We'd love to start a conversation. Fill out the form and we'll connect you with the right person.
Searching for a new career?
View job openings
